Biology - Cell structure
Cell structure
Mind map
mindmap
root((Cell structure))
Organelles all typical cells have
Cell membrane
Controls movement in and out of cells.
Outer membrane of cell
Semi-permeable
Cytoplasm
Where chemical reactions take place.
Surrounded by cell membrane
Gel-like mixture containing solutes, organelles, and water
Nucleus
Contains DNA and controls the cell.
Has a nuclear membrane, so DNA is not floating about
Mitochondria
Where aerobic respiration happens.
Folds: create lots of surface area for reactions
Ribosomes
Allows protein synthesis
Each cell contains thousands of them
Make proteins by translating RNA codes
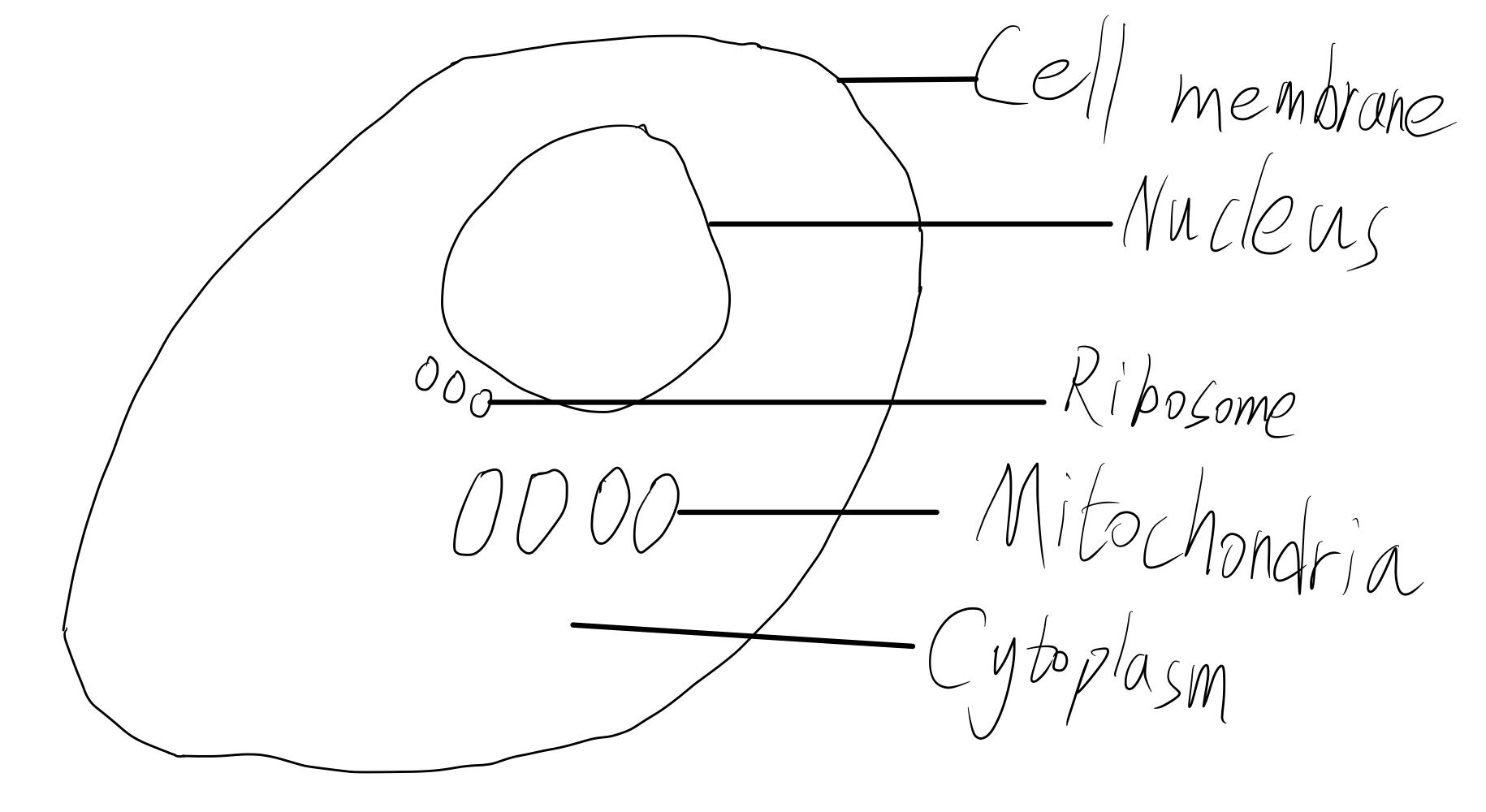
Animal cell
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Plant cell
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cell wall
Rigid to keep the shape of the cell, strengthens the cell.
Outermost layer
Permeable: They don't select who comes in and who leaves
Large Vacuole
Cell sap to keep cell turgid.
Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal
Contains water solution
Chloroplast
Contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
In green parts of plants
Prokaryotic cell
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Circular DNA
Instead of chromosomes, also called Nucleoid, is essential for controlling the activity and reproduction of the prokaryotic cell.
Plasmid
Small circles of DNA
Cell wall
Made of peptidoglycan not cellulose
Differences
Plant vs Animal
Cell Wall
Large Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Plant vs Prokaryotic
Nucleus vs Nucleoid and Plasmid
Cellulose vs Peptidoglycan
Organelles all typical cells have
Cell membrane
Controls movement in and out of cells.
- Outer membrane of cell
- Semi-permeable
Cytoplasm
Where chemical reactions take place.
- Surrounded by cell membrane
- Gel-like mixture containing solutes, orangelles, and water
Nucleus
Contains DNA and controls the cell.
- Has a nuclear membrane, so DNA is not floating about
Mitochondria
Where aerobic respiration happens.
- Folds: create lots of surface area for reactions
Ribosomes
Allows protein synthesis
- Each cell contains thousands of them
- Make proteins by translating RNA codes
Animal cell
Animal cell has all above.
Diagram
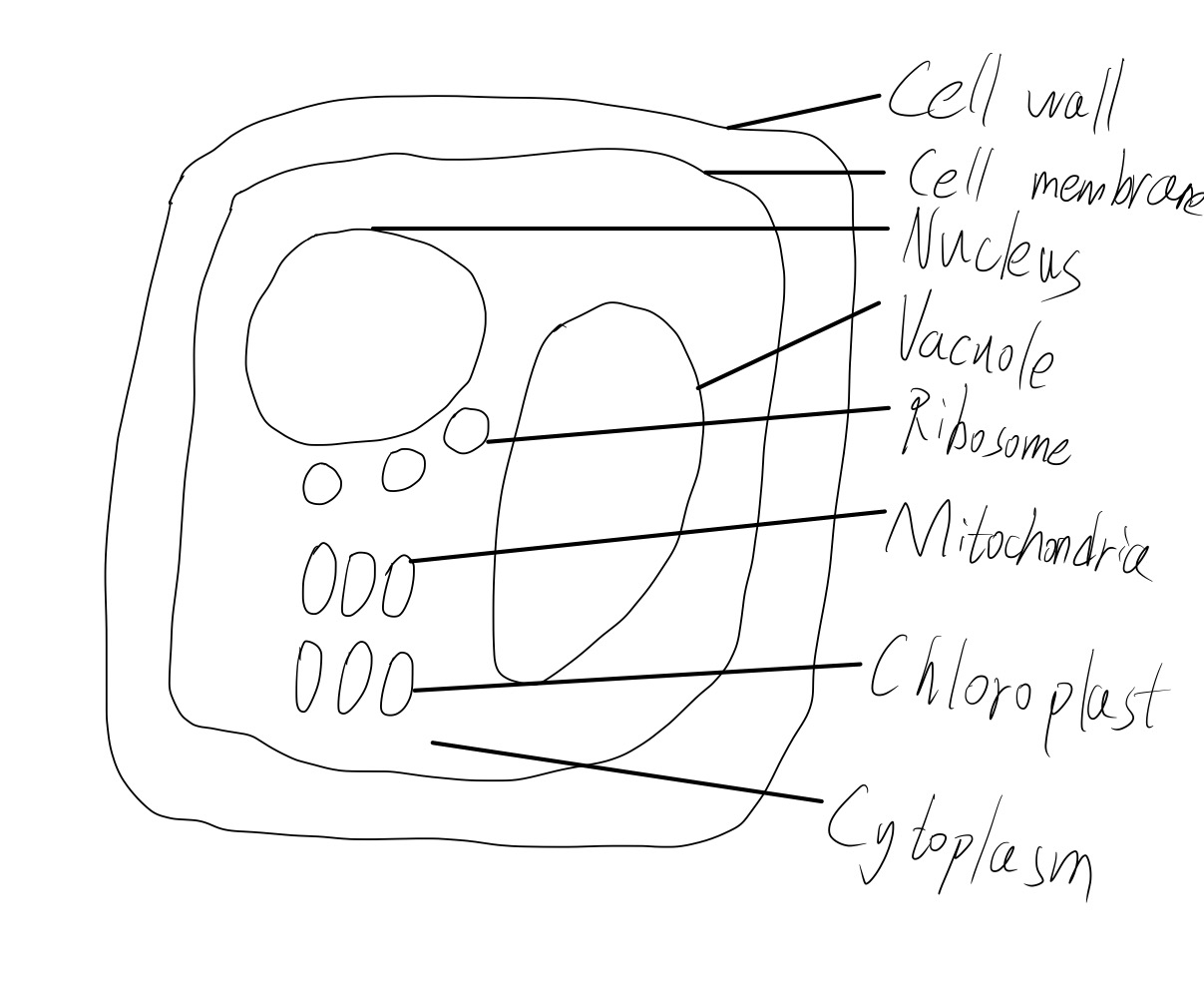
Plant cell
Plant cell especially also have:
Cell wall
Rigid to keep the shape of the cell, strengthens the cell.
- Outermost layer
- Permeable: They don’t select who comes in and who leaves
Large Vacuole
Cell sap to keep cell turgid.
- Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal
- Contains water solution
Chloroplast
Contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
- In green parts of plants
Diagram
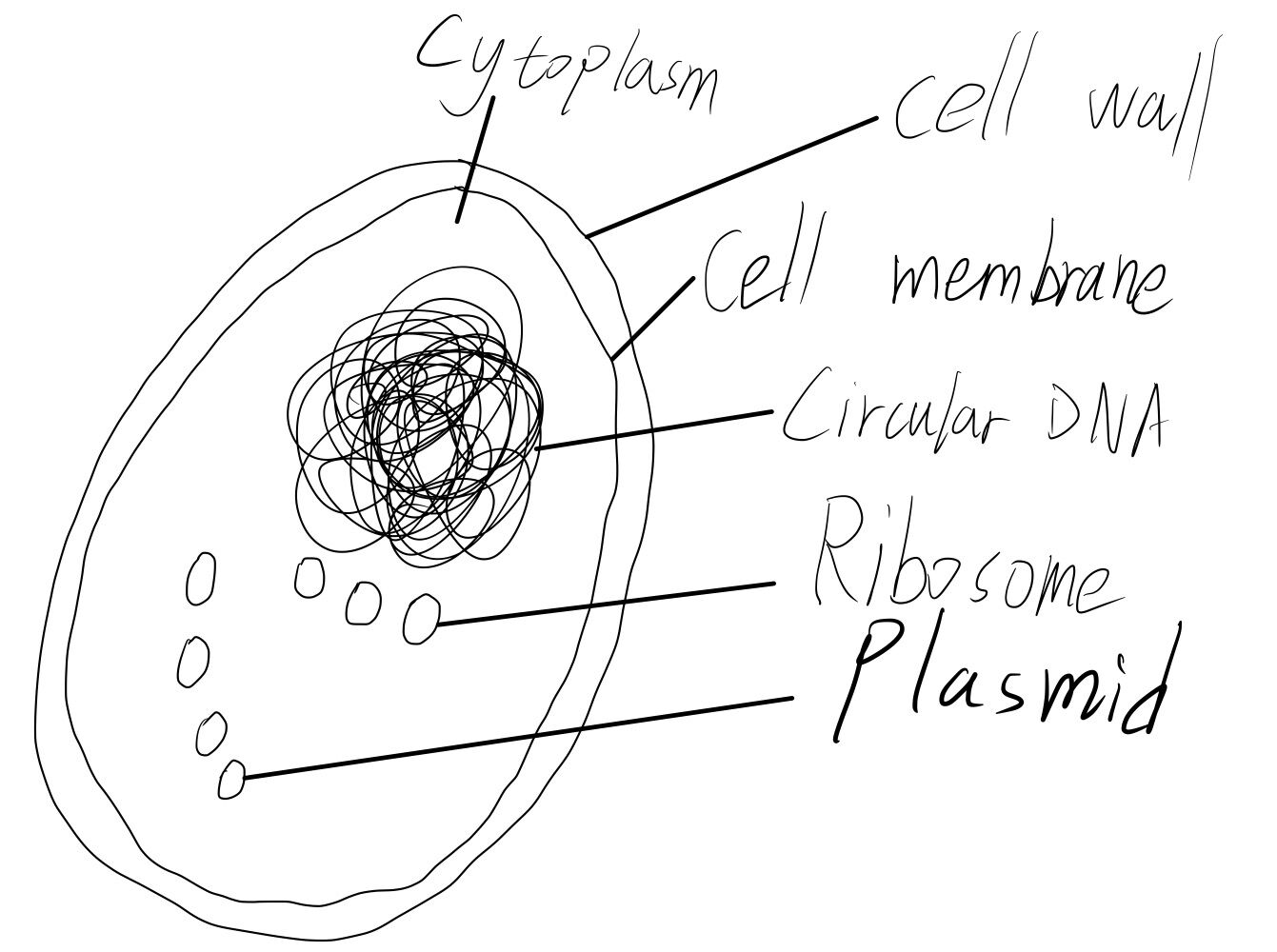
Prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cell do not have Mitochondria and Nucleus but organelles below.
Cell wall
Rigid to keep the shape of the cell, strengthens the cell.
- Made of peptidoglycan not cellulose
Circular DNA
Instead of chromosomes, also called Nucleoid, is essential for controlling the acticity and reproduction of the prokaryotic cell.
Plasmid
Small circles of DNA.
Diagram
Differences
Organelles in cells
| Organelles \ Cells | Plant Cell | Animal Cell | Prokaryotic Cell |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Yes | ||
| Cell Membrane | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Chloroplasts | Yes | ||
| Cytoplasm | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mitochondria | Yes | Yes | |
| Nucleus | Yes | Yes | |
| Ribosome | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Large Vacuole | Yes | ||
| Circular DNA | Yes | ||
| Plasmid | Yes |
Some differences between a plant cell and an animal cell
- A plant cell has cell wall, while an animal cell hasn’t.
- A plant cell has large vacuole, while an animal cell hasn’t.
- No animal cell has chloroplasts, but some plant cell do.
Some differences between a plant cell and a prokaryotic cell.
- A plant cell has nucleus, and a prokaryotic cell has nucleoid and plasmid instead.
- Cell wall in a plant cell is made of cellulose but peptidoglycan in a prokaryotic cell.
Biology - Cell structure
https://blog.cxzlw.top/2023/08/31/cell-structure/